Electric Power Problems
Electric Power Problems
Electrical Disturbances that cause our devices and systems to malfunction or interrupt their operation are classified as follows.
Power Quality Problem should be understood as "Source Voltage Waveform Distortion" . We can explain this in the figure below.
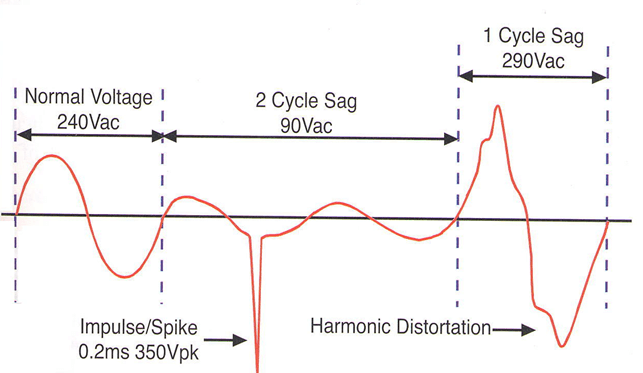
Spikes:
It is fast, short duration electrical transients superimposed on the utility voltage waveform.
Generally, it is caused by other devices with high current and switch-on and switch-off operations in the network.
This problem can result in hardware failure and data loss in software
Surges:
It is voltage increasing over the normal grid voltage for longer than a period (20 ms for 50 Hz Utility Voltage). Occurs during the disconnection of high power loads.
It damages the SMPS elements of the computer in a way that they cannot fulfill their functions.
Sags:
A voltage sag is a short duration reduction in utility voltage which can be caused by a short circuit, overload, or starting of high power electric motors. A voltage sag happens when the rms voltage decreases between and 90 percent of nominal voltage for one-half cycle to one minute.
If the voltage drops too low, restarting the computer can cause problems.
Brownouts:
It occurs when the utility voltage level remains at low levels for a long time (in some cases for hours).
Its effects are usually more serious than Sags.
It occurs as a result of the enterprise that generates electricity decreases voltage level of the whole system due to the increasing power requirement.
Electrical Noise:
Common mode (noise between phases and ground)
Normal mode (noise between phases and between phase and ground)
The causes of this problem are lightning, switch-on/switch-off of high power loads, cable faults and radio frequency devices.
It causes crashes of computers and destruction of data.
Harmonics:
Harmonics are multiples of the fundamental power frequency produced by the action of non-linear loads such as rectifiers, discharge lighting, or saturated magnetic devices.
Harmonic frequencies in the power grid are a frequent cause of power quality problems. Harmonics in power systems result in increased heating in the equipment and conductors, misfiring in variable speed drives, and torque pulsations in motors and generators.
Flicker:
It is defined as the changing of the frequency of the utility voltage as minus-plus 2-5 Hz range.
It is caused by loads that cause rapid reactive power changes such as arc furnaces.
Vibration in fluorescent lamps is its typical result.

